When did Amazon start selling things other than books?
As we have already seen, Amazon started out selling books online. This was groundbreaking for the time, and very few companies were providing the convenience that Amazon.com had to offer.
 Amazon sells many different items today.
Amazon sells many different items today.
But, when did it start selling other products? After following Bezos’ initial business plan, the company expanded into selling computer games and music in 1998. Simultaneously, Amazon expanded its services internationally by purchasing other online bookstores in the UK and Germany.
By the turn of the Millenium, Amazon had further expanded into selling consumer electronics, video games, software, home-improvement items, toys, games, and much more. By the mid-2000s, Amazon had launched its (AWS). This innovation fitted well with Bezos’ initial ambition to make Amazon a tech company rather than an online retailer exclusively.
The company’s expansion into digital services like EC2 and S3 would boost the company’s revenues significantly. Today, they remain the bulk of the income for Amazon Web Services.
 Amazon’s meteoric rise is one of businesses most impressive stories.
Amazon’s meteoric rise is one of businesses most impressive stories.
Technology[]
- Main article: Technology in the Amazon Empire
The Amazonians are skilled mathematicians and astronomers. They have discovered telescopes and most recently calculus. Such mathematical planning was required in building the hunting grounds which furthered the development of their civilization.
Bordering much of the Amazon River are large stone enclosures which confine wild herds to certain areas. What makes this practice revolutionary is that it is a method of farming while avoiding the effects of the Miasma. The Amazon Empire contains thirty of these hunting grounds.
The Amazonians themselves live in stone spires which dot the borders of these hunting pens. These spires are apartment complexes that house much of the richer population, and are decorated with intricate carvings of gargoyles.
The Amazon Empire is landlocked, and shipbuilding is largely limited to river travel, delivering goods from one spire to another.
Amazon introduces better business financing
Amazon is no stranger to looking for new growth opportunities, especially regarding its financial service offerings. Amazon Lending was launched in 2011 to provide small businesses with easier access to financing solutions in the U.S. The program includes term loans, business lines of credit, and interest-only loans for qualifying merchants. By 2018, Amazon Lending partnered with Bank of America Merrill Lynch to issue loans ranging from $1,000 to $750,000 for borrowers. But in 2019, the company shifted gears to partner with Goldman Sachs and offer credit lines up to $1M, including a digital application process and instant approval notification. Although this program is invite-only, Amazon’s Lending is available in the US, UK, Germany, Canada, China, France, India, Italy, and Spain. Amazon’s efforts to build a portfolio of financing tools for their merchants’ business needs didn’t stop here. By 2020, Amazon had invested more than $18 billion in the success of its third-party selling partners, including tools, services, programs, infrastructure, and people.
Since Amazon already offered financing opportunities for small and medium businesses, it was an easy shift to do the same for individual consumers by launching the Amazon Prime Secured Card in 2019. This initiative by the e-commerce giant acts to solve one of the biggest barriers to shopping on its website: lack of a credit card. More than a quarter of U.S. households have no or limited access to checking and savings accounts. These unbanked and underbanked households rely heavily cash or checks to fund purchases, creating a barrier to seamlessly shopping online.
Through a partnership with Synchrony Bank targeting the unbanked and underbanked populations, Amazon marketed this closed-loop card to customers with bad or no credit history. The card program includes receipt of a digital and physical card, an initial security deposit between $100 to $1,000 at the customer’s choice, has no annual fee, and offers Prime members 5% cashback on Amazon.com purchases. This secured card program also includes credit builder and tracking tools. The initial deposit determines customer credit limits as Synchrony Bank reports payment history to all three credit bureaus to improve customers’ credit scores through card usage.
With this service, Amazon has nailed weaving rewards programs and incentives into essential financial products and services that underbanked customers can more easily access and utilize. Beyond this, Amazon is providing financial resources and opportunities to a financial class of both customers and small businesses who are essentially left behind when it comes to qualifying for credit card services or financing through traditional banks. Amazon continues to spearhead financial digital inclusion for customers who may have been previously unable to take part in the digital economy, leaving no stone unturned for new customer acquisition, improving customer loyalty and increasing customer lifetime value.
Raising the bar with Amazon Prime
With the ingenious introduction of the Amazon Prime customer loyalty program in 2005 came a remarkable rise in customer appreciation, engagement, retention, and loyalty for the Amazon brand. Currently, prime memberships are available in 23 countries. The $14.99 monthly subscription includes benefits like free two-day delivery of eligible items, Prime Video, Amazon Prime Music streaming, free gaming, free grocery pick-up at Whole Foods, free ebooks, and the recent addition of a free year of Grubhub+. This move to reward customers for constant engagement has catapulted customer lifetime value for Amazon’s business. The brand reeled in $25.21 Billion in annual revenue from retail subscription fees, acquiring 200 Million active Prime members with the incentive to easily shop, pay, and indulge in entertainment all in one place.

As a perk exclusive to Prime membership, Amazon offers its customer base a wide array of co-branded card products. These cardholders are more likely to spend more with Amazon, increasing marketplace sales, boosting customer loyalty, and attracting new members with cash-back rewards and brand partnership discounts and benefits.
Amazon card partnerships:
Amazon Prime Store Card — Launched with Synchrony Bank in 2015, this was Amazon’s first card exclusively for Prime customers, offering unlimited 5% cash back on Amazon purchases.
Amazon Store Card — This is the standard version of their original card for non-Prime customers. It does not offer the 5% cash back perk or as many benefits as the Amazon Prime Store Card.
Amazon Reload — This reloadable digital debit card is available only to Prime members and offers 2% cash back on Amazon purchases. The card links directly to a customer’s checking account and reloads on a recurring or one-time basis.
Both versions of the Amazon Store Card are closed-loop, which means the cards can only be used at Amazon.com, Amazon-owned businesses, including Audible, Amazon Bookstore, Amazon Web Services, and places that accept Amazon Pay. The brand soon extended its financial service offerings again with an open-loop card partnership with Visa to launch a rewards debit card to be used anywhere for both Prime and non-Prime members.
Amazon Prime Rewards Visa Signature Card — Launched in partnership with Chase in 2017, this card gives Prime members 5% cash back at Amazon and Whole Foods, 2% cash back at gas stations, restaurants, and drugstores, and 1% cash back on everything else.
Amazon Rewards Visa Signature Card — This is the standard version of their rewards card for non-Prime customers. It offers 3% cash back on Amazon and Whole Foods purchases, 2% cash back at gas stations, restaurants, and drugstores, and 1% cash back on everything else.

Amazon Prime continues to pave the way for premium card loyalty programs, building an ecosystem that’s increasingly valuable to its members, along with the option for new customers to join via a free trial with their first purchase. This feature allows customers to take advantage of the benefits that interest them most immediately, and this incentive keeps them continually interacting with Amazon’s products and services.
Through Amazon Personalize introduced in 2018, the brand leverages machine learning and predictive data analytics with API technology to give every customer personalized recommendations for their shopping experience each time they visit the platform. As a powerful customer engagement tool that creates personalized recommendations as customers browse and shop on the platform in real time, it includes specified product recommendations, impressions data, customized direct marketing, and personalized product ranking across Amazon’s retail, entertainment, and media sectors in each customer’s Amazon account.
These real-time analytics help Amazon understand what behaviors drive their high-value customers as they continually optimize the retail experience, adjusting to customers whose wants and needs will shift over time. The utilization of machine learning allows Amazon’s value proposition to expand as its business grows, maintaining the relevancy of the platform into the future.
Amazon has built a brand experience that remains front and center, and as customers’ lifestyles change, the benefits of Amazon Prime will also evolve. Amazon Prime solidifies customer lifetime value with personalized user experiences that are highly targeted, resourceful, and always relevant for customers as they shift and move forward in life.
The Power Debate
Amazon has been accused in many quarters of retaining God-like power over the companies that sell on their platforms. The documentary examined these accusations and the further accusations that Amazon’s AWS services, with the purchase of companies like Ring and The Washington Post, made the company poised to usher in a dystopian future much like Geroge Orwell’s 1984.
The documentary publicized the reality of what sellers on the Amazon platform face by exploring the reasons behind Amazon’s notorious standoff with Hachette, which used to be one of the world’s biggest publishers. The documentary revealed how this dispute essentially split Amazon’s customers (readers) and authors/publishers along battle lines. While the Hachette dispute was later settled somewhat amicably, it set the tone for how Amazon conducted itself as it expanded its third-party seller program into all types of goods and industries. The documentary reveals that Amazon has the final say on which accounts go or stay.
Amazon’s list of banned or suspended accounts is growing every day. Still, Amazon argues that these bans protect the platform’s security, as evidenced by the ban of over 3,000 Chinese sellers in 2021 for security concerns. However, there have also been many complaints from all other parts of the world about a seeming indiscriminate attitude towards banning or suspension. A banned account on any other platform may not be a big deal, but for massive sellers like Midocommerce, it is the same as losing a million-dollar business empire and potential million-dollar deals at any given time.
«It is scary the power that Amazon has over its sellers, Their phenomenal system attracts a huge segment of the worlds sellers, but then they own the customers and retain great influence, including things like price. Amazon can put you out of business in seconds,» Perozo explains.
Midocommerce co-founders Eberths Perozo (LEFT) and Andres Corona (RIGHT).
Midocommerce
«The only way around this is to be extremely cautious and to understand how Amazon works. One of our selling points at Midocommerce is our deep knowledge of the platform, we have walked the lines, been blown up by landmines and lost money in the past as individual sellers. However, it has gotten us prepared for the brave new world of commerce championed by Amazon, there is no way of fighting it now, and so we have built solid systems. So far Midocommerce has zero suspensions and zero duplicate accounts or deactivated accounts, which shows how far we are willing to go to forgo fast profit in the interest on longevity and security.»
«While we can be proud of our expertise, every ecommerce entrepreneur needs to watch the documentary and be wary of the power Amazon holds.» Andres adds, «It is a textbook case of building an empire on borrowed land.»
VAN HORN, TEXAS — JULY 20: The New Shepard Blue Origin rocket lifts-off from the launch pad … carrying Jeff Bezos along with his brother Mark Bezos, 18-year-old Oliver Daemen, and 82-year-old Wally Funk prepare to launch on July 20, 2021 in Van Horn, Texas. Mr. Bezos and the crew are riding in the first human spaceflight for the company. (Photo by Joe Raedle/Getty Images)
Getty Images
Amazon’s growth has been unprecedented in American commerce; as it stands, the company sells almost everything there is to sell, including the ‘Amazon Empire’ documentary, which heavily criticizes Amazon as a company. Considering that the company is now effectively in every industry and retains an interest in space domination, it becomes interesting to speculate where the company will be in another decade or more.
What’s next? Possibilities for Amazon
Amazon has pursued digital payments innovation time and time again as the brand supports its customers’ financial needs directly through its platform. We just explored all the financial service offerings Amazon has to offer, and they leave nothing on the table except for one thing. Their customers are already using Amazon’s digital wallets, Amazon visas and secured cards, Amazon financing and loans, Amazon Pay to store their private bank information, and more. So why hasn’t Amazon just become its own bank?
With the mastery of customer personalization through Amazon Prime and Personalize, the financial versatility behind Buy with Prime and Amazon Pay, and Amazon Lending and Credit connecting with undertapped consumer markets, the company has all the working parts of a bank, including the capital to support further expansion of its financial operations.
Currently Amazon is still outsourcing financial services through traditional banking institutions and co-branded card partnerships. To manage any card or financial line of service offered through Amazon, customers still have to go directly through the issuing bank for questions, concerns, or issues, causing significant disruption in streamlining the customer experience. This also means Amazon is sacrificing valuable first-party data and insights from card usage to customer spending behavior outside of their platform and cannot fully capitalize on interchange revenue because that is still being collected by the bank.
With the right embedded finance partner, Amazon could directly own, automate, and fully control all of its financial service offerings from delivering their own branded cards, and virtual accounts to lending and instant global remittances. Amazon wouldn’t need to be co-sponsored by any bank and be held captive within a bank’s restrictive rules and regulations on consumer qualifications for financing, credit, and lending. The brand could create their own baseline for qualifying customers, and by becoming their own banking entity would bring customer experiences with their financial services full circle.
Amazon сегодня
Может показаться немного странным, но следующие десять с лишним лет (до наших дней) сайт amazon.com пережил без каких-либо особых потрясений и резких скачков. Увеличивалась капитализация ресурса и ассортимент магазина, открывались новые представительства в разных странах мира и расширялся штат сотрудников — всё это происходило как-то естественно и безболезненно. Получается, что взяв однажды рынок под свой контроль, Amazon уже не оставил лидирующей позиции.
Сегодня Амазон — это колоссальная корпорация с оборотом порядка 20 млрд $ в год и чистой прибылью порядка 0,5 млрд $. На сайте реализована масса технологичных сервисов, работают мощные отделы рекламы, аналитики, информации. Это уже онлайн-империя какая-то, которая начиналась с одного деревянного стола и старенького компьютера. И талантливого человека, которого зовут Джеффри Безос. Надеюсь, теперь вы это имя запомните!
Автор и эксперт: Алексей Востров.
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
10 октября 2020 года
Не завтра, но через 20 лет: важность долгосрочного мышления
По словам Безоса, величайшая сила Amazon — желание оставаться непонятым. Это относится и к бизнес-модели. Многие говорят, что Amazon терпит небольшие, но частые потери. Однако, компания думает в долгосрочной перспективе и спокойно терпит убытки, если они помогают достичь будущих целей.
Чтобы клиенты были счастливы, необходимо вести честную игру — считает Безос. Пусть это стоит больших денег в краткосрочном периоде, зато повышает лояльность клиентов, что в конечном счёте принесёт компании прибыль.
Пример. Когда электронные книги начали набирать популярность, Безос решил продавать их по $ 9,99. Amazon приобрели копии электронных книг по цене, равной печатным аналогам, и компания теряла около $ 5 на одной проданной книге. Безос пошёл на это, так как был убеждён, что рано или поздно издателям придётся снизить цены, и хотел сделать Amazon лучшим рынком электронных книг. Благодаря этому компания заработала первый миллиард долларов и обеспечила Kindle сенсационный успех.
Amazon отличается от других компаний своей ориентацией на долгосрочную перспективу. С самого начала Безос был одержим грандиозным видением и знал, что на его реализацию потребуются десятилетия.
How Did Bezos Do It?
“We are willing to be misunderstood for long periods of time.” – Jeff Bezos
Perhaps the most enthralling element of the Jeff Bezos story is his resolute commitment to executing a long-term vision, all while the rest of the world could not comprehend it.
The company ran 20 years without showing signs of significant profit, and it was regularly criticized in the media. Pundits saw Amazon as a growing online book store that couldn’t make money. They didn’t get the bigger picture.
And while the world debated Amazon’s aggressive expansion and polarizing nature, Bezos and his team stayed focused on execution. Even if people didn’t see the vision for the “everything store”, it didn’t mean that Amazon couldn’t build it.
They were willing to be misunderstood for a long time in order to follow the vision – one that was written down by Bezos in a famous napkin sketch:
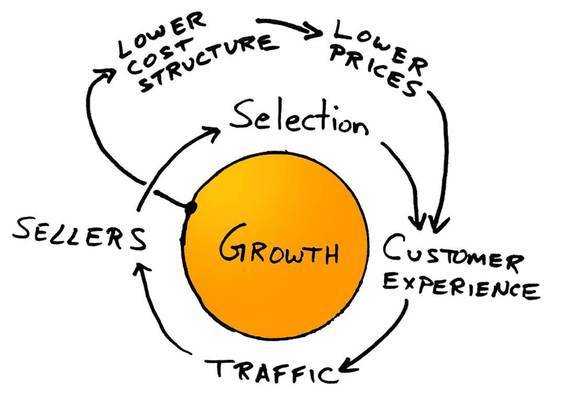
Image courtesy of: Amazon
Note that in this sketch, which is now over 15 years old, that there is no “take profits” offshoot. It’s a closed loop that uses free cash flow to reinvest back into the established business plan of providing low cost leadership.
And now that Amazon has executed on this plan successfully, it is finally time for profits. That’s why the company had a record quarter earlier this year, and why analysts expect Q2 to be just as impressive.
Watch out Warren, because Bezos isn’t done yet.
Триллионная капитализация на обмане
Американский ИТ-гигант Amazon на протяжении нескольких лет обманывал стартапы, воруя у них идеи для использования в собственных сервисах. Об этом пишет авторитетное издание Wall Street Journal (WSJ), приводя реальные примеры.
Как сообщает WSJ, у Amazon есть две схемы обмана небольших компаний-стартапов, один из которых даже позволяет ей не тратить ни цента на приобретение нужной ей технологии. Используя эту схему, Amazon устраивает встречу с представителями заинтересовавшей ее компании якобы с целью переговоров о возможной ее покупке. В рамках встреч она выясняет нужные ей детали, после чего стартап в итоге остается и без денег, и без уникальной идеи.
Второй способ требует от Amazon затрат денежных средств, она тоже неоднократно использовала его. Он подразумевает реальные инвестиции в компанию и получение доступа к информации о ее разработках на правах инвестора. Эти сведения она оперативно интегрирует в свой существующий или новый продукт, составить конкуренцию которому небольшой стартап уже не в состоянии, после чего он вынужден покинуть рынок.
 Основатель Amazon Джефф Безос (Jeff Bezos)
Основатель Amazon Джефф Безос (Jeff Bezos)
Amazon входит в число крупнейших ИТ-компаний в мире с капитализацией более $1,4 трлн на 24 июля 2020 г., по данным Yahoo Finance. Кроме того, она является лидером на мировом рынке облачных сервисов со своим Amazon Web Services (AWS), значительно опережая по доле рынка Microsoft и даже . По итогам I квартала 2020 г. платформа удерживала 32% глобального рынка, второе место заняла Microsoft с 18-процентной долей, а третьей – Google (8%). Выручка AWS за весь 2019 г. превысила $35 млрд.
Столы из дверей и первые мечты
Судьба если и не забрасывала Безоса подарками, то уж точно была к нему благосклонна. Главным преимуществом, которым обладал основатель «Амазона», было редкое умение не замыкаться в одной области. Так, он не только прекрасно разбирался в программировании, но ещё и здорово умел вникать в суть экономических процессов. Этакий эрудит, которому всё на свете любопытно и почти все даётся легко.
После недолгих раздумий Безос принял решение создать магазин по продаже книг, сделавшись удобным посредником между издательством и читателям. Сейчас эта модель кажется естественной, а в 1994 году это было настолько свежо и ново, что не было никакой гарантии успеха.
На первых порах проект запускался за счёт собственных накоплений и денег, которые Безос получил от своих родителей. В качестве главного офиса выступала небольшая комнатка, где стоял деревянный стол, сколоченный из кусков двери, и старенький компьютер. Это сегодня штат сотрудников Амазон насчитывает пару десятков тысяч человек, да и огромное офисное здание в Сиэтле поражает воображение, а начиналось же всё более чем скромно.
Л
- а). сайтов в то время было мало;
- б). магазин изначально задумывался как место, где покупателям должно быть удобно.
К тому же книга — оптимальный товар для удалённых продаж, поскольку она невелика и не требует слишком дорогостоящих затрат на доставку.
Меньше — лучше: чрезмерная бережливость
Такой лозунг не слишком уместен для Amazon, но подходит компаниям, начинающим работать в гараже и пытающимся выжить с минимальной рентабельностью. Amazon характеризуется бережливостью, которую некоторые считают чрезмерной. Однако, Джефф Безос уверен, что ограничения провоцируют инновации, а бережливость позволяет сосредоточиться на важнейших вещах (например, удовлетворенности потребителей).
Сотрудники Amazon самостоятельно платят за парковку; на работе им не предоставляются бесплатные закуски; в командировках приходится спать в двухместных номерах, а менеджеры сами платят за билеты на самолет. В целом корпоративная культура Amazon суровая и очень конкурентная. Девиз компании: «Вы можете работать долго, усердно и эффективно, и в Amazon нельзя выбрать лишь два варианта из трёх».
Пример. В центрах реализации Amazon работники ежедневно наматывают до 30 километров в поисках товаров. При этом они очень молчаливы — их могут уволить за разговоры друг с другом.
В Amazon неоднократно нанимали десятки тысяч временных работников, особенно в разгар сезона (например, перед Рождеством), а затем увольняли. Подход Amazon прост: центры открываются в экономически слабых районах, где им рады, поскольку считают, что это улучшит местное экономическое положение. А Amazon всего лишь использует возможность нанимать дешевую рабочую силу и увольняет работников по окончании сезона, понимая, что компании они больше не нужны.
Prime benefits beyond Amazon
Buy with Prime is a newer service launched in April 2022. It allows Prime members to order items through other retailers’ websites using payment and shipping information stored on their Amazon account with a one-click purchase capability. This service also enables free delivery, a seamless checkout experience, and free returns on eligible orders backed by Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA). As this new incentive attracts more customers, it also empowers other companies to promote the Amazon brand while scaling their businesses at lower costs.
Amazon brand loyalty is further extended into new markets as this program completely shifts the utility of the Amazon Prime membership. Buy with Prime sets a new standard for customer convenience, elevating the online shopping experience via a multichannel proposition that benefits Amazon, the merchants, and, most importantly, their customers.
Amazon’s mission to be “Earth’s most customer-centric company” is a vision that has successfully come to fruition. The brand’s global reach in e-commerce, financial technology, and customer loyalty has reimagined the digital shopping experience. While Amazon continues to raise the bar on the competition and maximize its success, it’s evident that embedded financial services have played a significant role in the evolution and growth of the Amazon empire.



















![Кому принадлежит больше всего акций amzn? [решено]](http://grandcapital73.ru/wp-content/uploads/4/4/3/443e7573d36829e0fd923140089fccb4.jpeg)








