Введение
Появление концепции «носимой электроники» связано с развитием целого ряда технологий. В первую очередь она обязана достижению высокой степени миниатюризации и интеграции электронных компонентов, обеспечивших малые размеры для носимых устройств и появление новых сфер применения и сервисных функций. Высокий уровень интеграции, развитие рынка мобильных устройств, новых технологий — все это способствовало возникновению новых областей потребления. Электронная техника перемещается из разряда переносной или портативной в разряд постоянно носимой и обеспечивающей комфортный уровень функционирования человека. Носимая электроника имеет широкий спектр применений: развлечение, коммуникации и связь, военное снаряжение, медицина и здравоохранение, спорт, мода, обеспечение личной безопасности и пр.
Устройства носимой электроники появились достаточно давно. Первыми из таких устройств стали наручные электронные часы. Вторым стало появление мобильного телефона, а третьим — мультимедийного плеера, с возможностью записи и воспроизведения цифровых, аудио- и видеоданных.
В настоящий момент носимые устройства имеют огромные вычислительные ресурсы, достаточные для автономного решения владельцем комплексных задач различного плана. Встроенные микродисплей, видеокамера, персональная связь, интегрированные устройства ввода данных и управления, датчики и актуаторы — все это обеспечивает широчайший спектр устройств носимой электроники.
Их можно разделить на несколько категорий: концептуальные модели, изготовленные в единичных экземплярах для демонстрации потенциальных возможностей конкретной технологии, и серийные изделия, предназначенные для рынка. Последние также разделяются на два сектора — массовые и дешевые изделия для широкого применения и дорогие — для специфического рынка.
Судьба новых технологий на первом этапе зависит от эффективности первого применения, которое привлечет внимание массового потребителя. В маркетинге его называют killer application — «убойным приложением»
Чтобы продавать новый вид товара, сначала необходимо показать его ценность возможным покупателям.
Для того чтобы концептуальная модель со временем стала killer application, требуется несколько составляющих. Во-первых, должна созреть потребность на рынке в данном виде услуг и товаров, обусловленная появлением новых функциональных возможностей, заложенных в данном товаре. Для развития данной составляющей существуют как объективные, так и субъективные факторы. К объективным относится реальная потребность общества в данном виде услуг и товаров. Сдерживающим фактором может служить первоначально высокая цена изделия, низкая надежность и малая функциональность. К субъективным — активное навязывание модного товара с низкой функциональностью за счет формирования модного стиля жизни и искусственного развития потребления. Собственно, все вышесказанное справедливо по отношению к внедрению любых новых технологий. В экономическом аспекте концепция носимой электроники может открыть дверь и для других технологических революций, подобных Интернету или мобильной связи.
Функциональные возможности носимой электроники:
- коммуникации и средства связи;
- аудио- и видеосредства;
- идентификация личности;
- персональная навигация;
- обеспечение безопасности;
- мониторинг биологического состояния;
- поддержка комфортного состояния пользователя.
Сферы применения носимой электроники:
- бытовая электроника, досуг;
- военный сектор;
- медицина (рис. 1), здравоохранение и спорт;Рис. 1. Монитор сердечного ритма Polar (информация о внешней среде при помощи функции определения уровня спуска или подъема, учета скорости владельца, альтиметра, барометра и компаса)
- персональная безопасность;
- промышленный сектор;
- транспорт;
- мода.
Основные компоненты носимой электроники:
- компьютерные модули;
- модули персональной связи;
- источники питания;
- полимерные материалы;
- технология межсоединений;
- встроенная в одежду система датчиков для распознавания жестов и поз и положений тела;
- встроенные источники тепла;
- светоизлучающая ткань;
- гибкие дисплеи для встраивания в одежду.
Wearable Technology – First Virtual Reality ‘Headset’
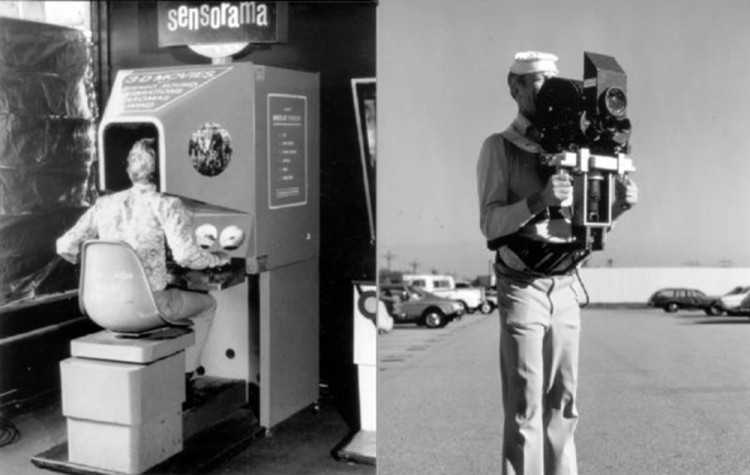

Past world war two, the history of wearable technology touches down the year of 1960. We find Morton Heilig, a cinematographer that has just created a new way of enjoying movies through what he calls the “immersive arcade experience.”
It is the first recorded attempt at blending cinema with virtual reality. Morton called his invention the “Stereophonic Television Head-Mounted Display” and patented the invention.
Two years later, in 1962, he patented another invention. The “Sensorama Simulator” (US Patent #3.050.870). An upgraded virtual reality simulator, with handlebars, binocular display, vibrating seat, stereophonic speakers, cold air blower and a device close to the nose that would generate odours, all synchronised with the action in the film.
Now if this does not make you think of the 4DX technology, stop now! Go to the cinema, see “The Hunger Games” and only then come back for more of the history of wearable technology.
And, when your seat starts shaking, remember that Morton Heiling invented the same tech, half of a century ago. Minus the comfy cushions, but you get the idea.
What can Wearable Technology do?
At the moment, wearable technology serves many purposes, but in comparison to other types of technology, it is a newer medium that is still being developed and experimented with. The most common uses for wearable technology (as we stated earlier) are for helping to monitor and alert the wearer about their personal health information or for social communication purposes – like calling, texting, social media, etc.
But there are other purposes and possible functions of wearable technology that many people are unaware of. Wearable technology can be used to improve and treat mental health issues like depression and anxiety. These devices usually come in the form of a wristband that sends periodic electric pulses to either remind you to think, feel or do something or to

Classification of wearable computers
We won’t get into the history of what is wearable computer. One need only know that the conception isn’t new and it has been vigorously promoted since 1960.
Smart glasses
One of the variants of a wearable mobile computer is so-called smart glasses, the tangible model of which was first created by the American inventor Steve Mann. The image is usually projected onto the inside of the wearable computer glasses, replacing or augmenting the visual picture of the environment.
Smart glasses are produced by a number of global companies such as Google, Epson, and Vuzix. A typical device is a stereo-wearing or mono-screen mini-computer with a web camera, various sensors, Internet access, IP telephony features and other capabilities.
Perhaps, the most famous and multifunctional device is Google Glass (some of the functions are implemented via a Wi-Fi smartphone).
The entertainment opportunities of the augmented reality of such a device are ample: identifying the faces of the surrounding people and comparing them with the photos of the friends of the account on the social network; display the shortest path for motorists, etc.
Smart watches
Smart watches can include a camera, accelerometer, thermometer, barometer, compass, chronograph, calculator, mobile phone, touch screen, GPS navigator, speaker, scheduler and others. Some watches have the functionality of fitness trackers. Such models can support training programs, route tracking, heart rate sensor.
Like other computers, smart watches can collect data using external or built-in sensors. They can manage or receive data from other devices or computers.

HMDs
Some vendors produce HMD with onboard operating systems, e. g. Android, enabling applications to run locally on the HMD, and eliminating the need to bind to an external device for generating video. Such head-mounted displays are sometimes called smart glasses mentioned above. By the way, there is no consensus about where is the borderline between the HMD and the smart glasses.
Smart clothing: future of wearable computers
Smart clothing, or smart garments, is one more category of wearable computers that are gaining momentum.
Here are explicit advantages of smart garments by contrast to other wearables:
- flexibility;
- implemented invisible sensors;
- there is no need for additional devices except clothing;
- a large surface of the body for reading out data.
High-end smart garments are produced of stretching material, can be printed on a 3D printer (conductive inks), is washed without removing sensors, contains implemented sensors that track numerous types of data at once.

Innovative smart clothing can perceive not only disaggregated data types, but also make forecasts and adapt to the external environment without preliminary adjustment. Such clothing functions like human brain thanks to the built-in microcomputer.
TESLASUIT believes that it’s smart clothes that will replace mobile phones and will become the future of wearable computing devices. There is already a plethora of different types of smart clothing by items.
Also if you are interested in more detailed info about smart clothing and want to know what place smart garments place on the playing field of the wearables market, move to our smart clothing market review.
Wearable Technology – First Wearable Camera

Let’s now check out a multi-million company, conceived in the back of a VW van dubbed “The Biscuit.” The company I am talking about is now called GoPro, with a valuation of 3.86 billion U.S. dollars last year.
So, before we had extreme sports athletes, police officers and even drones fitted with GoPro cameras, we have tried the wearable cameras on birds. I am serious. Pigeon photography was a technique invented in 1907 by a German apothecary, Julius Neubronner.
The pigeon was fitted with an aluminium breast harness and a very light, time-delayed miniature camera. This simple invention let the German army capture game-changing aerial photographs, behind the enemy lines.
What exactly is wearable tech?

The new age of wearables tap into the connected self – they’re laden with smart sensors that track our movements and biometrics, often using Bluetooth to sync wirelessly to a smartphone. Others also rely on Wi-Fi connectivity and standalone mobile 4G LTE data connections.
Wearables use sensors to connect to you as a person, helping you to achieve goals such as staying fit and active, losing weight, being more organized or tracking your overall mental and physical health. In the case of VR and AR heads-up displays, they’re providing a wealth of new entertainment and educational opportunities, as well as enhancing the world around us.
How do you wear them?
The early generations of wearables saw devices clipped to our bodies, as the prime focus was tracking movement through motion sensors. However, advancements brought a wide-range of powerful sensors, which require direct contact with the skin. Thus, the tech gravitated to other body parts: the wrists, fingers, chest, forearms, ears, eyes, forehead, temple and anywhere else you can think of (yes, even those parts).
Implantables
Implantables make contact with the user’s body from the inside, rather than on the skin. For instance, the now-bankrupt company Proteus produced sensor-containing pills that could monitor blood pressure and other health metrics; after the patient swallowed the pills, they could wear an external device to easily monitor the data generated from within the body. In the near future, smart tattoos may also become available for patients who want an easy way of ensuring that they always remember to bring their monitoring devices with them.
Why you should know about implantables: For work involving technology-sensitive components (for example, magnets), companies often need to clarify policies for employees using older implantable devices such as pacemakers. New kinds of implantable technology will add new logistical wrinkles to safety guidelines, and as such, businesses should research new implantable devices and update their safety protocols accordingly.
Ключевые элементы
На данный момент носимые компьютеры во многом считаются витком эволюции смартфонов, которые наиболее близки к «носимой» технологии сами по себе. Но ее реальная история, как мы знаем, уходит далеко за то время, когда был изобретен первый сотовый телефон, не говоря уже о первых смартфонах. В тех больших и громоздких устройствах можно разглядеть корни современных носимых компьютеров: камеры и PC.
Влияние компьютеров и, в частности, персональных компьютеров, очень сложно переоценить. Как блестяще заметил исследователь и гейм-дизайнер Ян Богост (Ian Bogost) в недавнем эссе для The Atlantic, которое было посвящено Алану Тьюрингу, компьютер – это устройство, созданное не для выполнения конкретного задания, но для имитации других устройств, или «особый вид машины, который работает, выдавая себя за другую машину». Чем мощней и совершенней становятся компьютеры, тем больше устройств они могут имитировать и, в конечном счете, заменить.
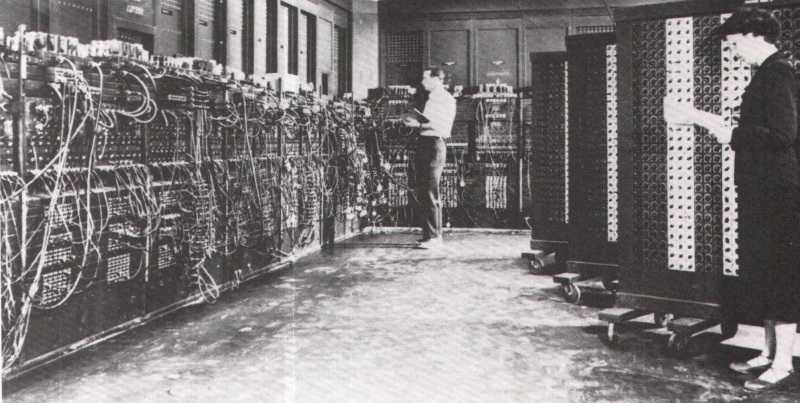
ENIAC – первый электронный цифровой компьютер общего назначения
С появлением персональных компьютеров это стало еще более очевидно, т.к. все меньше людей отдавали предпочтение радио, телевидению, калькуляторам и множеству других девайсов. Совсем недавно мы наблюдали похожую картину, когда люди переключались с PC на смартфоны, планшетные компьютеры, камеры и игровые консоли. В каждом из этих случаев новая технология вымещала старую и начинала играть все более важную роль в жизни людей. В то время как персональные компьютеры были этаким вычислительным центром, привязанным к дому, смартфон стал почти постоянным аксессуаром и источником непрерывной связи. Носимые компьютеры обещают и далее расширять идею «перманентного соединения»
И что более важно, их потенциала достаточно, чтобы полностью изменить природу того, что мы называем «связь»
Еще одно ключевое и не менее важное устройство – это камера. Как некогда мобильное и всегда (или почти всегда) доступное подключение к интернету дало толчок развитию смартфонов и отделило их от персональных компьютеров, так и сейчас постоянно активная камера – это один из ключевых факторов отличия смартфонов от многих современных носимых компьютеров
Это не всегда было так очевидно, так как многие носимые компьютеры были специализированы для выполнения конкретных задач. Например, устройство, которое многими по праву считается самым первым носимым компьютером, было задумано в 1955 г., а протестировано в 1961 г. Эдвардом Торпом с целью помогать владельцу при игре в рулетку. Безусловно, это был носимый компьютер, т.к. один из элементов устройства был встроен в ботинок и управлялся при помощи пальца ноги, а другой представлял собой наушник, в котором проигрывалась та или иная музыкальная нота. Данный девайс выполнял некие базовые вычисления (расчет времени шарика и колеса рулетки), но его создатели не задавались целью сделать именно носимый компьютер. Когда грянула эпоха PC, нашему глазу предстали новые идеи для wearable-технологии, а также четкие признаки того, что как раз камера сыграет в этом существенную роль.
Носимый компьютер без камеры – это просто компьютер, который можно носить с собой. Он более портативен, всегда доступен и будучи таким, какой он есть, открывает новые возможности, но эта идея не ушла далеко от традиционных персональных компьютеров. У него есть экран, один-два устройства ввода и ряд программ для выполнения тех или иных задач. Но если добавить камеру, носимый компьютер становится не просто девайсом для съемки и записи, но устройством для постоянного мониторинга окружающего пространства (плюс некоторая помощь со стороны GPS и всевозможных сенсоров). Такая ситуация делает проекты вроде Glass все более значимыми. То, что мы обычно видим перед своими глазами плюс наложение дополнительной информации – это не просто какая-то очередная новинка, на которую интересно посмотреть. Это новый способ смотреть на окружающий мир.
Хранение звонков, смс, интернет-трафика
А вот, пожалуй, и пункт, который вызвал наибольшее негодование среди граждан. Операторы связи должны хранить все звонки абонентов, а также их сообщения за период, который определяется правительством (на текущий момент – 6 месяцев). Также операторы должны хранить всю информацию о фактах приёма, передачи, доставки и обработки сообщений и звонков за последние три года.
Все интернет-компании и интернет-сервисы (Одноклассники, ВКонтакте и т.п.) должны хранить следующую информацию: псевдоним (логин), дата рождения, адрес, ФИО, паспортные данные, языки, на которых общается пользователь, список его родственников, все аудио- и текстовые сообщения, видеозаписи, адрес электронной почты, дату и время входа и выхода из информационного сервиса, полное название программы-клиента, которой пользовался абонент. Всю эту информацию интернет-компании и сервисы должны предоставлять спецслужбам.

Но это ещё не всё. Операторы связи, оказывающие телематические услуги (то есть услуги через интернет, например, электронная почта, мессенджеры и т.п.) обязаны хранить все переданные через них сообщения и файлы. Срок хранения сообщений и файлов – 30 суток. Каждый год в течение 5 лет этот срок должен увеличиваться на 15%.
Защитные акции российского рынка — 2023
Я уже упоминал о важности стабилизации портфеля в 2023 году защитными акциями — бумагами, которые в значительной степени сохраняют свою стоимость при обвалах рынка и снижают общие потери инвестора (подробнее объясняю суть в отдельной статье: Защитные активы). Поэтому отдельно выделю защитные акции российского рынка — 2023
Это высоконадежные компании, слабо зависящие от санкций, с хорошей дивидендной историей, низким или отрицательным коэффициентом бета (показывающим зависимость от рынка в целом)
Поэтому отдельно выделю защитные акции российского рынка — 2023. Это высоконадежные компании, слабо зависящие от санкций, с хорошей дивидендной историей, низким или отрицательным коэффициентом бета (показывающим зависимость от рынка в целом).
- Фосагро (лидер сектора, слабо завсисит от санкций, высокие дивиденды, низкая волатильность, росла во время обвала в 2022 году);
- Норникель (лидер сектора, мировой лидер по некоторым позициям экспорта цветных металлов, слабо зависит от санкций, платит дивиденды, низкая волатильность);
- Полюс (лидер сектора, коррелирует с ценой золота как основного защитного актива);
- МТС (лидер сектора, ориентирован на внутренний рынок, слабо зависит от санкций, высокие дивиденды, низкая волатильность);
- ОГК-2 (ориентирован на внутренний рынок, слабо зависит от санкций, высокие дивиденды);
- Россети (ориентирован на внутренний рынок, слабо зависит от санкций, потенциально высокие дивиденды, низкая волатильность);
- Сургутнефтегаз АП (потенциально высокие дивиденды, выигрывает от падения рубля, низкая волатильность).
Также при выборе, в какие акции инвестировать в 2023 году — в акции роста или акции стоимости, я бы отдал предпочтение акциям стоимости, ввиду пониженных рисков. Гоняться за доходностью, опережающей рынок, в нынешних условиях считаю крайне рискованной идеей.
Предпочтительными считаю акции с хорошей дивидендной историей, отдельно написал подробный прогноз по дивидендам российских компаний на 2023 год. Средняя дивидендная доходность рынка в 2023 году может сохраниться на уровне 10% или даже вырасти на 1-2%.
Вот такие перспективы развития российского фондового рынка в 2023 году вижу я. В заключение еще раз напомню, что мое личное видение не является индивидуальной инвестиционной рекомендацией, все решения о покупке и продаже активов вы должны принимать исключительно самостоятельно.
Оставайтесь на Финансовом гении и учитесь грамотно зарабатывать, тратить, сохранять и приумножать личные финансы. До новых встреч!
Оценить:
Wearable Technology
Wearable technology, often known as “wearables,” refers to a class of electronic devices that may be worn as accessories, incorporated into clothing, placed in the user’s body, or even tattooed on the skin. The gadgets are useful, can be used without using your hands, and are capable of transmitting and receiving data through the Internet.
Wearable technology has been around since the 13th century when the first sunglasses were made. Since about 1500, people have been able to wear small clocks. But the definition of current wearable technology is that it has a microprocessor and a way to connect to the internet.
The development of mobile networks made wearable technology possible. The first big wave of wearable technology that caught on with customers was fitness activity trackers. Then, the watch turned into a screen, and better mobile apps were added. People can get information from Wi-Fi networks with Bluetooth headsets, smartwatches, and glasses that can connect to the web. With virtual reality and augmented reality headsets, the gaming business is adding more things that can be worn.
Smart Clothing
By making contact with a larger amount of one’s body, smart clothing can provide deeper insights than other examples of modern wearable technology can, enabling advanced tracking for both medical care and lifestyle improvement. Samsung conducts extensive research in this sector, and has filed a number of promising patents; if these patents become commercially-available products, Samsung may soon release smart shirts capable of diagnosing respiratory diseases and smart shoes that monitor running form. Consumers can already purchase Siren Socks (smart socks that can detect developing foot ulcers), Nadi X smart pants by Wearable X (yoga pants that vibrate to improve form during yoga exercises), and Naviano smart swimsuits that provide alerts when the user should apply sunscreen, among many other kinds of smart clothing.
Enterprises have also begun to use smart clothing as a way to generate brand loyalty. In a unique example of wearable technology, Tommy Hilfiger experimented with adding location-tracking functionality to its Tommy Jeans Xplore line of clothing. This enabled the clothing to track how frequently the customer wore it, so Tommy Hilfiger could reward frequent wearers with more Tommy Hilfiger products.
Why you should know about smart clothing: In the coming years, businesses will need to review their dress codes and decide whether or not to allow smart clothing in meetings, networking events, and other contexts. Anticipating potential questions from employees and updating dress codes ahead of the trend will solve issues about wearables technology before they arise.
Wearable Technology – First Commercial Wearables
Google Glass. A pair of smart glasses also called a head-mounted Android smartphone. On paper, Google Glass project was groundbreaking. In reality…Let’s just say that the trial release of the Glass did not go quite as expected.
There were major privacy concerns, endless headache complaints, and even reports of potential addiction caused by the use of the glasses for prolonged periods of time. Don’t know how, as the battery on mine never lasted more than 45 minutes on a single charge.
Not long before the Glass, in 2008, Fitbit, a wearable tech startup, launched its Fitbit Classic wristband. A fitness tracker that allowed the wearer to monitor the taken steps, the travelled distance, the kilocalories consumed, intensity levels, and sleep patterns.
It was the start of a new era, the use of wearable tech in fitness, healthcare, and even fashion thanks to the new generations of smartwatches, smart jewellery, and luxurious fitness trackers.
Designing the Future of Wearable Technology
As the landscape of wearable technology expands and matures, designers will have new opportunities to influence how people interact with the digital world. New technology succeeds best when it fits into or enhances natural human behavior. This is true for every interface platform, not just wearables.
These devices are not meant to be interacted with in the same way as a laptop or a smartphone. Designers must consider how they are worn and how they can most discretely and efficiently gather and deliver information for the wearer. Some wearables even influence how other people react to their wearers, for better or worse. In many cases, the best wearable devices disappear gracefully into the background.
Wearable Technology Trends looking forwards
I’m not going to make any predictions here rather merely sum up what I have read and seen.
Healthcare
I think the biggest thing looking forwards multiple years will be the growth in implantable smart devices available. Going forwards it won’t be just pacemakers and defibrillators but all the artificial hips, legs, arms etc. will surely at some point get sensors and start communicating. When some body part or organ is replaced in the body it will be more likely that it will not just do what the original part did but rather have some additional capabilities and augment the human features in some way.
Wearable accessories
In the short term we are bound to see more and more devices with smart capabilities and communication built in. Smart watches will keep improving, but all the other things we wear like glasses, jewelry, clothes, helmets, shoes will start getting new features.
Personally I would enjoy getting better gear for swimming. A reliable way of tracking swimming distance and showing the distance and lap times on my goggles would be amazing. There is a South Korean company called Zwim working on some smart goggles and I really hope they will be good.
Current trends converging on wearable computing devices
Moving from wrist wearable computer
Maybe for now wristbands and smartwatches are the most popular items among wearable computers but another trend looms on the horizon in the long term. Embedding sensors in daily things is the success factor for wearables. And the most evident item that we put on everyday basis is clothing.
A study by Forrester showed that almost 30 % of respondents want to wear devices clipped on clothing and 15 % would like it embedded. The last thing is not very common yet, but potential customers are ready for them.
Wearable computers for fitness and healthy lifestyle is growing in popularity
People involved in sports and tracking their health are the most common consumers of wearables. Reading such types of data as ECG, EMG, temperature, breath characteristics, pace, speed, sleeping patterns, etc and analyzing them is extremely important for athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
Services and applications for fitness and health generate high profits as wearables are not only for consumers but also for healthcare systems and businesses that want to monitor activity and provide recommendations for patients and employees.
A gold mine for retailers
Soon wearable computers will know all or most of the info about our experience, habits, inclinations, and preferences. This plays into the hands of retailers that collect big data. Considering the fact that for now all wearables are connected with smartphones, collecting personalized data is a tendency that will contribute to ubiquitous and right on target advertising.
Focus on design
This is not just about UX and usability, but also about individual style. Millennials are especially convinced that devices underscore their personality. In general, the aesthetics of things, and in particular wearables, is extremely important as a key factor of a purchase decision.
Wearables are developing in this direction moving from bulkiness and producibility and turning into light everyday devices. Moreover, wearable computing devices are more likely to take form of fashionable clothing and jewelry.
Wearables will direct a drive to IoT
Wearable computers track different parameters of the environment, record them and analyze with the help of AI. Wearables are particularly apt for environmental management as they are always with users and are most likely to replace smartphones for this function.
Wearables and cloud computing
More and more companies are moving their entire data centers to the cloud. This process makes the data integration easier not only for consumers but also for cloud-based data centers that are able to collect, track, and collate enterprise data automatically.
The collected data may be used to support the performance of individuals or teams, forecast timeframe for future business projects, and to encourage the achievement of high-level employees.
So, hope now you have a more holistic view of what is wearable computer. In case if you are really interested in the world if wearables, advise profound reading of wearables market overview.
Published on: 23 Aug 2018
Updated on: 26 Sep 2022
Author: v.padasinavik@teslasuit.io
Tags: Smart clothing, wearables
Share to:
What is meant by Wearable Technology?
Wearable technology is a type of electronic device or equipment that can be worn on the body (i.e. like a wrist watch, a belt, jacket, etc.), implanted in one’s body (i.e. a heart monitor, birth control chips, etc.) or in some cases tattooed on to your body (i.e. a tattoo that lights up or changes colors). What defines wearable technology is the no-hands-needed aspect. Most wearable technologies use microprocessors to function and have the ability to send or receive information using wifi and other internet tools.
The first ever external wearable technology device was invented in 1961 by Edward Thorp and Claude Shannon. It was a four button wrist “watch” that and was originally designed to help them cheat at a game of roulette. But because wearable technology includes tech that is implanted in one’s body, some could argue that the first wearable technology device invented was the pacemaker in 1960, by a group of VA researchers.

Today, the most commonly known and used wearable technology are Smart Watches. Many tech companies have their own version, but the most popular by far is the Apple Watch. Other companies that have their own version of a Smart Watch include Samsung, Garmin, Polar and Fitbit.
Smart Jewelry
This includes things like rings, necklaces, earrings, bracelets, etc. and are most commonly used as sensors that sync and communicate with a smartphone app to send health information.
Smart Clothing
Smart clothing has been developed collaboratively by the fashion industry, tech engineers and medical professionals for decades. Today the most common type of Smart Clothing uses special fabrics infused with technology that can track, record and communicate your biometric data.
Smart Glasses
Over the years, many companies have tried to launch their own version of Smart Glasses. The first company to release this product was Google in 2014 and it did not do well. This specific type of wearable technology has had a low success rate over the years and is still being developed by companies like Facebook, Google, Samsung and more.
Мотивация
Критикующие пакет представители либеральной общественности указывают на ужесточение ответственности за уже имеющиеся в Уголовном кодексе правонарушения, введение новых и расширение полномочий правоохранительных органов. Однако представить дело так, как будто Яровая и Озеров просто перемигнулись и решили придумать что-то эдакое, сатрапское, для того чтобы удушить демократические свободы граждан России, даже у них не получается. Страна, как и весь мир, к сожалению, испытывает угрозы и вызовы, что видно по европейским терактом, поэтому законодатели просто действуют на опережение, чтобы в дельнейшем по возможности избежать необходимости подсчитывать число жертв. И не рисовать потом мелками на асфальте жалобные надписи. Естественно, некоторые свободы ради этого придется ограничить, и, судя по внесённым в проект изменениям, имело место обсуждение рациональных способов определения степени разумности принимаемых мер. Возможно, авторы проекта даже несколько увлеклись, но их поправили, а соображения их признаны в целом оправданными. Так и подобает работать над законами в демократическом обществе.

Специализированные и практические приложения
Несмотря на некоторые провалы, например, Google Glass, акцент в развитии носимых технологий сместился в сторону более специализированных и практичных применений. Имплантаты микрочипов теперь используются для замены ключей и паролей. Эти имплантаты, вживляемые в кончики пальцев, используют технологию связи ближнего поля (NFC) или радиочастотной идентификации (RFID), подобно чипам, используемым для отслеживания потерявшихся домашних животных.
Однако наиболее жизненно важные применения носимых технологий можно найти в области медицины. Одним из ярких примеров является Cyrcadia Breast Monitor — интеллектуальный пластырь, способный обнаруживать ранние признаки рака груди и передавать информацию в лабораторию для анализа. Носимые мониторы медицинского оповещения обеспечивают большую мобильность и независимость пожилым и ослабленным людям. Кроме того, разрабатываются «умные» татуировки с гибкими электронными датчиками для мониторинга сердечной и мозговой активности, нарушений сна и работы мышц.
Voice User Interface (VUI) and Wearables
In the past, designing a Voice User Interface (VUI) was particularly difficult. In addition to the challenges inherent to voice recognition, due to their transient and invisible nature, VUIs are also fraught with major interaction hurdles.
Unlike visual interfaces, once verbal commands and actions have been communicated to the user, they are gone. One approach employed with moderate success is to give a visual output in response to the vocal input, such as on a smartwatch (Siri on an Apple Watch, for example). Still, designing the user experience for these types of devices presents the same limitations and challenges of the past.
When speaking with machines, a human user may miss the natural feedback loop of human-to-human conversation used to establish shared understanding. They will try to give a command or ask for something, hope the machine will understand what they’re saying, and give back valuable information in return. Most current voice AI is not sophisticated enough to build on the communication to reach understanding and may not be able to distinguish a new command from a clarification on a previous one.
Moreover, speech today as a means of human-computer interaction is still exceptionally inefficient. For example, it would take too long to verbally present a menu of choices. Users cannot visually track the structure of the data, and they need to remember the path to their goal. When presenting choices in a visual UI, designers lean on Miller’s Law and usually present a maximum of seven options. That maximum drops significantly when a user is expected to remember a list of options delivered verbally.
For VUI, the challenges are real. A sensible approach is to incorporate support for voice interaction but to limit its use to those places where it is most effective, otherwise augmenting it with interface mechanisms that employ the other senses. VUI will continue to improve and is a great option for visually-impaired accessibility. Accepting verbal input and providing visual feedback are the two most effective ways to incorporate a VUI into the overall user experience.






























