What is Open Banking? Definition
Open banking is the practice of facilitating safe interoperability in the banking sector by permitting third-party payment services and other financial service providers access to financial transactions and other data from financial firms. Through application programming interfaces or APIs, third-party businesses may access the data.
As the global financial system continues to change, open banking is growing in popularity. This is because it enables faster, protected national and international transactions while offering customers far more options for managing their funds by utilizing third parties.
The approval and implementation of PSD2
In October 2015, the European Parliament passed the European Payment Services Directive, otherwise known as PSD2. This new regulation was passed with the goal of creating a single payments market, in line with the European Union’s goal of standardizing laws and regulations across Europe, and promoting innovation, competition, and greater efficiency in the online payments space. The law came into force for the 27 EU countries on 13 January 2018, with a transition period that ended in September 2019.
In 2020 and 2021, more European banks have been implementing APIs, with a big rise in third-party providers. In the UK, there are already 300 third-party providers involved in Open Banking.
Why is the UK so advanced when it comes to Open Banking? Let’s take a look.
¿What is Open Banking?
The concept of Open Banking comes from the idea of “open innovation”, a term promoted by Henry Chesbrough in 2005 which has strong links with the changes in the attitude towards data ownership, which crystallized into the GDPR and the Open Data movement.
The Open Data movement refers to the idea that certain types of data should be available for everyone, without copyright restrictions, patents, or other control mechanisms.
Open Banking is an extension of this idea. The premise is that personal banking data should be more accessible so that companies and individuals can leverage it in different ways to provide better services and offer more benefits to customers.
To adapt to this new reality, promote competition on the market, and promote Open Banking, the European Union passed a new directive on financial payments in 2015, PSD2, updating the legislation from 2009.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does open banking help me get a loan?
The loan application process typically involves filling out an application that a bank analyzes for accuracy and creditworthiness. Open banking gives potential lenders instant access to your account, so they can analyze the information they need as soon as you complete your application.
What information is shared with open banking?
Generally, open banking shares payment and account information. You have some level of control over what data is shared and who gets to see it. Regulatory bodies are considering a standard that could determine exactly who can see your information and how they must ask for your consent. Some areas in Europe have already imposed these rules.
Privacy Issues
Open banking relies on sharing data, but you might prefer to keep your information private. Fortunately, open banking should not automatically reduce security or privacy. TPPs and banks would need to take steps to protect confidential information and to educate consumers about the new risks they face.
Data Sharing
Open banking initiatives typically specify when and how financial institutions can share your data. For example, U.K. regulators require customers to approve of information-sharing with specific parties. U.S. banks already control (and limit) how your information is shared, with input from you, and they don’t seem eager to give up that ability.
Any sharing you authorize puts your information into somebody else’s hands. Then you need to wonder how effective that TPP will be at protecting your information—and what they’ll do with the data.
Тренды мобильного банкинга 2023
Сегодня мобильное приложение — это главное средство привлечения и удержания пользователей. Больше половины клиентов предпочитают пользоваться услугами банка через приложение. Поэтому основная задача бизнеса — наращивать функционал, используя инновационные банковские технологии.
Персонализация
Аналитики Gartner ожидают в 2023 рост персонализации цифрового офиса. Банки продолжат расширять возможности аналитики, чтобы лучше узнать пользователя. Сбор данных о клиенте для формирования кастомизированных предложений и улучшения пользовательского опыта, перенос взаимодействий с банком и функций физического офиса в онлайн, формирование экосистемного подхода являются одними из основных трендов в сегменте.
Мобильный интернет-банк
Весной этого года некоторые российские мобильные банки были удалены из сторов. Это событие повлекло за собой миграцию пользователей из приложений в мобильные версии интернет-банков. Не все успели адаптировать интернет-банк. Мобильные версии интернет-банков достаточно сильно отличаются от привычных приложений визуально и функционально. Клиенты, чувствительные к качеству цифрового опыта, при переходе из приложения в мобильную версию интернет-банка могут испытывать критичные неудобства. В этом году банки будут совершенствовать пользовательский опыт в мобильных интернет-банках.
Чат-боты
Согласно исследованию
, число успешно обрабатываемых чат-ботами запросов за год выросло в среднем на 9-15% на каждый блок пользовательских сценариев. У чат-ботов все еще сохраняется репутация инструмента для решения простых задач, и когда речь идет о сложном вопросе, пользователь даже не пытается поручить ее текстовому роботу и сразу просит переключить на оператора-человека — несмотря на то, что бот вполне может справиться.
Чат-бот для предпринимателей от ПСБ умеет выставлять счета, оплачивать налоги штрафы, повторять платежи из истории, оформлять предодобренный кредит. Инструмент закрывает основные бизнес-потребности.
В 2023 банки будут дальше развивать чат-ботов, имитирующих разговор с реальным человеком и нацеленных на мгновенный ответ на запрос.
Сторис
Банки внутри своих приложений формируют контентные площадки с информационными сообщениями, индивидуальными предложениями и полезными сервисами. Тренд продолжит свой рост в 2023.
Через сторис банки продвигают свои продукты, рассказывают о полезных функциях, знакомят с новыми фичами. А некоторые успешно интегрирует не только финансовые, но и небанковские сервисы — авиабилеты, страхование, билеты на мероприятия, продажа товаров.
Цифровая доступность
Доступ к финансовым услугам — важная часть жизни взрослого человека. Каждый может столкнуться с ограничениями — травма, поездка за рулем, маленький ребенок на руках. Особенные потребности в России испытывает больше половины населения: 13 млн человек с инвалидностью, 37 млн пенсионеров, примерно 30 млн людей с временными ограничениями по здоровью. Создавая доступные мобильные приложения, банки закрывают потребности для половины населения страны. Это не только социальная ответственность для банка, но и конкурентное преимущество.
Open Banking API
В последние два года одной из инноваций финтеха стала технология Open Banking. Она открывает для банков много возможностей:
— Улучшает показатели вовлеченности и удержания клиентов.
— Дает возможность собирать и анализировать большее количество информации о клиентах и предлагать им персонализированные услуги.
— Более глубокий скоринг позволяет банкам выдавать больше кредитов по выгодным ставкам, что может привлечь дополнительную аудиторию.
Для пользователей банковских услуг Open Banking означает в первую очередь повышение качества услуг. Например, повышение скорости процессов и более дружелюбные интерфейсы, расширение продуктовой линейки и удобный поиск выгодных предложений.
Benefits of Open Banking
There are numerous factors that have made open banking an accepted norm for businesses across the board. It allows you:
1. Cut down transaction fees
Consumers seldom consider the costs retailers must pay to accept credit card payments. Each card transaction may incur up to ten to fifteen separate fees, which may drive up the price of products and services.
Open banking opened the door for account-to-account (A2A) payments, which enable consumers to make purchases directly from their bank accounts. Consumers may also connect accounts to a retailer’s mobile application or website and complete purchases with a single click. Purchasing straight from bank accounts eliminates any card processing costs, which is advantageous for retailers and customers both.
2. Improve offline retail experiences
Thanks to open banking, businesses may leverage payment initiation services (PIS) to optimize the client checkout experience. Previously, in order to use digital transactions at a retail store, customers were required to pay for products through an internet transfer from the merchant’s bank account. To do this, customers would have to open many tabs, copy and paste, or even manually enter account information. This payment process was cumbersome, hazardous, and time-consuming.
With the advent of open banking, fintech businesses have developed payment initiation services (PIS). Using a QR code or barcode, these innovative solutions enable customers to make secure purchases in just a few clicks and with no effort. These enhanced payment flows also boost sales, adding to the merchant’s advantage.
3. Avail more services due to data integration
All of your financial information, including financial transactions, bank cards, investments, debts, pensions, and more, consolidated in one location enables infinite possibilities. For certain users (like a small, local firm), favorable loan arrangements are often unavailable. Others may be refused credit altogether. With greater availability of banking data, however, previously excluded customers and organizations will now have access to some financial products and instruments.
4. Make transactions more secure
Strong customer authentication (SCA), the part of the payment journey in which the customer takes an additional step to validate the payment, has assisted in reducing fraud. However, it has been deployed inconsistently for card payments, resulting in long payment processes.
In contrast, open banking transactions were designed with SCA in mind. For customers, the authentication procedure comprises a simple redirect to the bank app, where they verify the transaction before being redirected to the merchant’s site to finish the transaction.
Open Banking Definition
Open banking is the practice of sharing financial information electronically, securely, and only under conditions that customers approve of. Application programming interfaces (APIs) allow TPPs to access financial information efficiently. This promotes the development of new apps and services and lets them be developed quickly and cheaply. Ideally, open banking should result in a better experience for consumers, as well as more sophisticated financial services or any program with embedded financial services.
You may already have used services that open banking would improve upon. For example, third-party personal financial management (PFM) tools like Mint use your bank account information to help you track spending and reach other goals. Or you might have already connected your bank account with an investment app or other subscription-based app using Plaid.
No More Screen Scraping
The first generation of PFM apps, also known as account aggregators, required you to provide the same user name and password you use to log in to your bank account. Then the app would be free to “screen scrape”—to pick and choose the information it needed from among all the info it had at its disposal. That was cumbersome and unreliable and required reworking after your bank updated its website. APIs, on the other hand, give apps direct access to the exact pieces of data needed: your account balance or specific transaction details, for example. What’s more, you don’t need to tell anybody your password.
Open Banking Benefits for Consumers
Consider your own financial life as a consumer. You likely have a combination of credit cards, debit cards, checking and savings accounts, insurance products, retirement accounts, and more across multiple financial institutions and fintech companies. There’s a lot going on. The typical consumer has an average of 5-7 different financial accounts. And, according to Cornerstone Research, it’s not uncommon for a young couple to do business with 30-40 financial providers.
Open Banking gives you the ability to access and act on your banking data, such as create a single view of your accounts and even make direct payments from these accounts. You can link bank accounts to loyalty programs, share data with accountants and advisors, and more.
Open Banking also creates more choice in the banking products and services you want to use. Data access and portability make it easier for you to shop around, compare products, and find the right banking solution to meet your needs.
For these reasons, the concept of open banking goes beyond financial institutions and fintech companies. More companies are adopting open finance APIs to build and offer digital products that help consumers and businesses understand their financial lives.
Зачем нужен
Open Banking приносит огромные преимущества как людям, так, самим банкам, другим компаниям. Вот некоторые из главных причин, почему он стал новым подходом к банковской индустрии:
- Расширение услуг, возможностей для клиентов: позволяет людям объединить данные со своих различных финансовых учреждений в одном месте. Это дает им лучший контроль над своими деньгами, предоставляет более точные аналитические инструменты для управления бюджетом, инвестициями.
- Создание новых сервисов: благодаря доступу к данным, финтех-компании, другие организации могут разрабатывать инновационные сервисы: персональные финансовые помощники, автоматические инвестиционные платформы.
- Стимулирование конкуренции: открытый доступ к данным позволяет банкам, другим фин.учреждениям предлагать более инновационные продукты, услуги. Это способствует конкуренции, поддерживает высокое качество услуг.
- Безопасность, защита данных: технология строго регулируется законодательством о защите данных. Компании, имеющие доступ к данным, обязаны обеспечивать высокий уровень безопасности, конфиденциальности.
Directives around the world
The United Kingdom, the leader in Open Banking
The United Kingdom is one of the European countries that is promoting Open Banking the most. In fact, one year after PSD2 was passed in 2015; the Competition and Markets Authority (CMA) issued a ruling that required nine of the largest banks in the UK (HSBC, Barclays, RBS, Santander, Bank of Ireland, Allied Irish Bank, Danske Bank, Lloyds, and Nationwide) to allow companies to access data from their transactions.
Under the scope of the UK Competition and Markets Authority (CMA), these banks created the Open Banking Implementation Entity (OBIE) to promote the opening up of financial data in the United Kingdom.
As such, British banks have been among the first to create open APIs that allow TPPs to access banking data. Meanwhile, the UK has also been a pioneer in issuing AISP and PISP accreditations to interested companies so that they can begin to operate under this new paradigm.
The British model in promoting Open Banking has been an inspiration for others, and many EU and non-EU states are now seeking to replicate it.
In 2021, more than 2.5 million UK customers now use Open Banking enabled products, and third-party API call volume increased from 66.8 million in 2018 to nearly 6 billion in 2020.
¿How does it work?
What the banks do
Following the implementation of PSD2, banks are now obliged to make their customer data shareable. That means that their customers’ data should be accessible via an API, which a licensed third party can then have access to.
Banks are currently working on their APIs, although some are moving faster than others. In the UK, the 9 large banks are all Open Banking compliant.
How you get registered
If you want direct access to your customers’ financial data, then you will need to get an AISP or PISP license. These can take up to a year to acquire and require rigorous regulation and compliance management.
Another easier, and better option is to instead partner with a financial company that already has all the licenses in place. Unnax, for example, has an AISP, PISP, and an EMI license — the only company in Spain to have all three. By partnering with us, you can connect with your customers’ data without having to acquire a license.
What the customer sees
What happens on the customer side? This depends on the action they are taking.
If they are pushing a payment via Open Banking, then they can make the transaction with an account to account payment instead of using their credit card. They would just need to pick their bank account from the list and complete payment in a few taps. These types of payments are especially suited to sectors with large ticket sizes such as travel, which many cards will block because of their built-in limits.
If it’s just account reading, then Open Banking allows them to view all their different bank balances on one screen. As a PFM or financial advisor, this can come in very handy.
Let’s dive a bit deeper into AISP and PISPs:
What is a banking API?
APIs are a set of codes and protocols that decide how different software components should interact – they essentially allow different applications to communicate with one another.
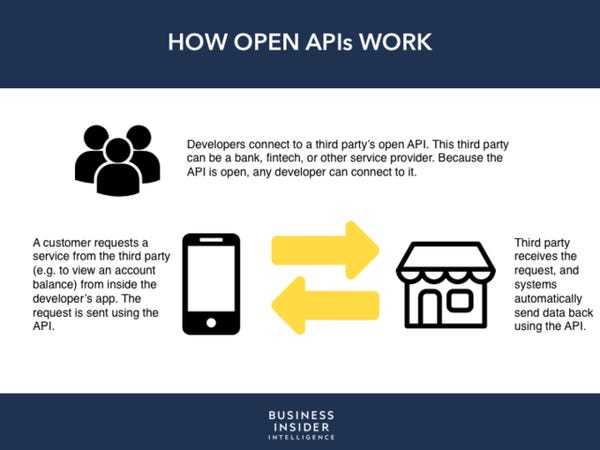 APIs are essential to open banking services.
APIs are essential to open banking services.
According to The Monetization of Open Banking Report from Insider Intelligence, APIs have been used to connect developers to payment networks as well as display billing details on a bank’s website. Through open banking, APIs are now being used to issue commands to third party providers.
APIs are also necessary for the functionality of Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) – a key component of open banking. BaaS is an end-to-end process that connects fintechs and other third parties to banks’ systems directly through the use of APIs. It helps to build up banks’ offerings on top of financial providers’ regulated infrastructure.
Like what you’re reading? Click here to learn more about Insider Intelligence’s leading Financial Services research.
Инновационные технологии в банковской сфере 2023
Новые банковские технологии обеспечили пользователям простой и удобный доступ к финансовым операциям. А переход от традиционного обслуживания к цифровому офису помог банкам оптимизировать расходы, улучшить сервис и повысить лояльность клиентов.
Простые платежи
В 2022 году пользователи смартфонов лишились возможности бесконтактной оплаты. В этом году конкуренция развернется вокруг решений, упрощающих процесс оплаты: pay-сервисов, QR-кодов, платежей по биометрии.
Также в 2023 вырастет спрос на платежные сервисы, которые включают в себя BNPL-сервисы, когда стоимость покупки разбивается на равные части и выплачивается в течение одного-двух месяцев, peer-to-peer платежи.
Сегментация аудитории
Сегментация — это мировой тренд финтеха, который усилится в этом году. Бизнес стремится предложить узкой аудитории решение, созданное специально под ее потребности. Например, сервисы для управления семейным бюджетом и детский банкинг.
Искусственный интеллект
ИИ далеко не новая технология в банковской сфере. Она активно используется банками для оптимизации бизнес-процессов, улучшения качества обслуживания. Например, для скоринга клиентов, финансового мониторинга, голосовых помощников.
Но предполагается, что расцвет технологии еще впереди. От скоринга мы уже перешли к персонализации обслуживании и оценки эмоций. Система на основе технологий машинного обучения распознает поведенческие паттерны в транзакциях клиента и его интересы к продуктам и сервисам банка в мобильном приложении практически в реальном времени.
В Альфа-банке искусственный интеллект анализирует данные о том, где открывать новые отделения. А «Открытие» использует ИИ для составления расписания сотрудников, которые занимаются продажами. Так клиенты могут заранее узнать комфортное для посещения время.
Кибербезопасность
В 2022 году вопросы количество кибератак на финансовый сектор выросло. В этом году банки продолжат повышать качество антифрод-процедур и налаживать выявление аномалий поведения клиентов с помощью ИИ и сопутствующих технологий — машинное обучение, сбор и обработка больших данных, открытые API.
Low-code
Всё более заметным становится тренд на Low-Code — подход, дающий возможность выпускать полнофункциональные решения быстро и с минимальным количеством написанного кода. По сути, процесс разработки становится похожим на строительство из конструктора, в котором все детали подходят друг к другу. Gartner
, что к 2024 году более 65% приложений будут создавать именно таким способом.
Benefits of open banking
Open banking has the potential to increase revenue streams while expanding customer reach for financial institutions – an opportunity incumbents shouldn’t ignore. It can also create revenue-sharing ecosystems, where incumbents give customers access to third-party-developed services while profiting from a subscription or referral basis.
Insider Intelligence projects the revenue potential in the UK generated through Open Banking-enabled small- and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) and retail customer propositions to reach $2 billion by 2024 – a 25% compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
Additionally, open banking allows banks to commercialize their infrastructure by moving into the BaaS space and providing core services to fintechs and other third parties.
Open Banking Benefits for Financial Institutions and Fintechs
Open Banking brings enormous benefits to financial institutions and fintech companies. Why?
- Customer-permissioned data sharing via Open Banking is bi-directional. This means that financial institutions and fintech companies receive and share data via an API, setting them up to unlock new value from the financial data. This helps foster innovation and uncover new revenue opportunities.
-
Open Banking tears down data silos. It provides financial services companies with greater insights into their customers and enables more efficient data sharing across departments. It also helps create a unified approach to digital identity management and reduces data resale and data exhaust issues. This can lead to:
-
- More Accurate Customer Profiles: Financial providers can gain access to real-time financial data from their consumers. They can easily see where consumers are sharing their data and why it is being used. This helps identify product and partnership opportunities.
- Enhanced Customer Experiences: By putting consumers in the driver’s seat, financial providers can build trust and improve relationships, leading to greater customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Personalized Services: By analyzing their financial data, businesses can identify specific customer needs or preferences and tailor their offerings accordingly. For example, a bank may offer investment opportunities to customers who have a higher disposable income, or provide budgeting tools to those who struggle to manage their finances. By offering more personalized services, businesses can create a stronger connection with their customers, leading to increased loyalty and retention.
-
- Open Banking brings added security by replacing sharing credentials (such as username and password) with credential-free, tokenized connections. Consumers must grant permission before their data is shared, including who has access and what data they have access to view. For example, customers setting up a budgeting app can grant permission to share a particular subset of data rather than share everything. By leveraging an open banking API rather than screen scraping, consumers never have to share their usernames and passwords, and financial providers eliminate the risk of sharing credentials.
What is open banking?
Open banking is a system under which banks open up their application programming interfaces (APIs), allowing third parties to access financial information needed to develop new apps and services and providing account holders greater financial transparency options. And this system is set to shake up the financial experiences for customers across the globe – in a good way.
While open banking allows third parties to develop better personal finance management (PFM) applications, it places pressure on incumbents to improve their own offerings. Open banking services cultivate competition in the banking industry – forcing incumbents to either enhance their financial services or partner with fintechs.





























